Antenna Types – Dipole Antenna
February 4, 2019
Dipole Antenna

Rabbit ears” dipole variant for VHF television reception

Two-element turnstile antenna for reception of weather satellite data, 137 MHz. Has circular polarization.
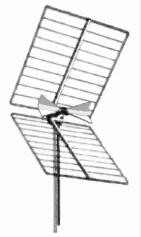
Corner reflector UHF TV antenna with “bowtie” dipole driven element at its center
The dipole is the prototypical antenna on which a large class of antennas are based. A basic dipole antenna consists of two conductors (usually metal rods or wires) arranged symmetrically, with one side of the balanced feedline from the transmitter or receiver attached to each. The most common type, the half-wave dipole, consists of two resonant elements just under a quarter wavelength long. This antenna radiates maximally in directions perpendicular to the antenna’s axis, giving it a small directive gain of 2.15 dBi. Although half-wave dipoles are used alone as omnidirectional antennas, they are also a building block of many other more complicated directional antennas.
Turnstile – Two dipole antennas mounted at right angles, fed with a phase difference of 90°. This antenna is unusual in that it radiates in all directions (no nulls in the radiation pattern), with horizontal polarization in directions coplanar with the elements, circular polarization normal to that plane, and elliptical polarization in other directions. Used for receiving signals from satellites, as circular polarization is transmitted by many satellites.
Corner reflector – A directive antenna with moderate gain of about 8 dBi often used at UHF frequencies. Consists of a dipole mounted in front of two reflective metal screens joined at an angle, usually 90°. Used as a rooftop UHF television antenna and for point-to-point data links.
Patch (microstrip) – A type of antenna with elements consisting of metal sheets mounted over a ground plane. Similar to dipole with gain of 6–9 dBi. Integrated into surfaces such as aircraft bodies. Their easy fabrication using PCB techniques have made them popular in modern wireless devices. Often combined into arrays.
[from wikipedia]
